India’s First Processor “SHAKTI” is Ready for App Development
shakti indian processor1
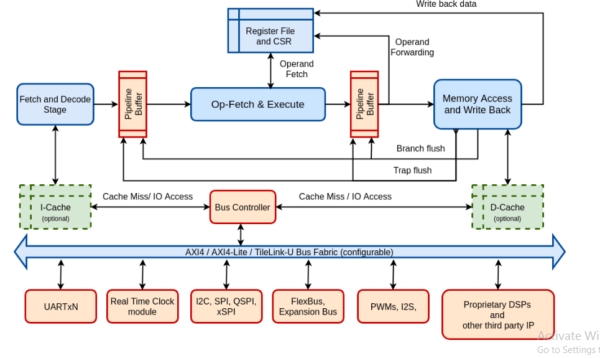
Shakti is India’s first homemade web processor recently launched by India. The chipset has been in the work field since 2016. The software development kit (SDK) has been released by IIT, Indian Institute of Technology in Madras for its open source “Shakti” processor.
This processor named Shakti is based on the open-source RISC-V instruction set architecture. The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, India has funded this processor. In addition to that IIT i.e the Indian Institute of Technology, Madras also promised that a development board will also be released in no time.
The developers can now begin to work on the development of applications for the Shakti processors along with the release of Shakti SDK.
For the development of Shakti, Only Indian Institute of Technology Madras’ RISE group is responsible. Moreover, they made an announcement that they will gonna release six different classes of this processor, soon in the market.
The six classes to be released will be:
● E class
● C class
● I class
● M class
● S class
● H class
These six classes can be used in a variety of devices such as IoT, on various robotic platforms, motor controls and much more.
Basically, the above stages of the processor have been divided into three categories as described below:-
1) BASE CLASS:
a) C-CLASS
This C-class is a 5 stage, 32 bit, in order micro-controller class of processors. It supports 0.2-1 GHz clock speed.
It is mainly aimed at mid-range application workloads. In addition, it has an extremely low power profile and hence includes support for optional memory protection.
b) E- CLASS
The E class is a 3 stage, in order processor made specifically for embedded devices like robotic platforms, (IoT) Internet of Things devices, motor controls, etc.
c) I- CLASS
This I class is a 64 bit, an out-of-order processor that supports 1.5-2.5 GHz clock speeds. It supports multiple threads. It targets storage, mobile, and networking applications.
2) MULTI-CORE PROCESSORS:
a) H-CLASS
These H class multi-core processors are designed primarily for analytics and high- performance computing workloads. The primary features include optional L4 cache, a high single thread performance, and it supports storage class memory and Gen-Z fabric.
b) M-CLASS
The multi-core M class’s processor supports up to eight CPU cores. The CPU Cores can be I as well as C class cores.
c) S- CLASS
This S class of multicore processor is basically meant for server-side and workstation type workloads. It can also be termed as an advanced version of another I class processor that supports multi-threads.
3) EXPERIMENTAL PROCESSORS
This category of stages are designed primarily as experimental nature and includes variants of
the base-class processors modified to meet specific criteria.
a) T-CLASS
It supports object-level security and coarse grain tags for micro-VM-like functionality to mitigate software attacks. For example Buffer-overflow.
b) F- CLASS
It is basically also an advanced version of T class processor with some additional support for ECC memory, redundant compute blocks and bus fabrics and a feature to detect those faults which are permanent.
Author: Prachi K
Technical Writer, Branding Executive – Hackers Interview. Prachi has professional experience in the area of Branding and Article writing.



